Session Objectives:
At the end of this session the students will be able to
- Identify the heat transfer modes and their application for solving engineering problems
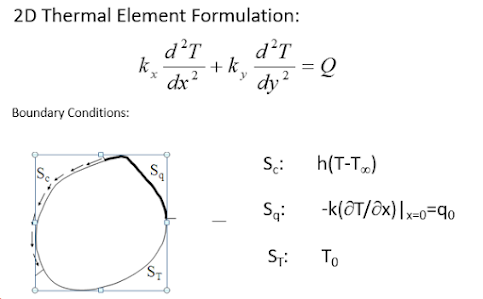
- Formulate 1D, 2D and 3D elements for solving thermal analysis problem
- Apply proper boundary conditions for solving thermal problems
- Use different solution algorithms to solve set of linear equations
- Interpret the finite element solution results with proper post processing steps
Physics:
The science of matter and energy and of interactions between the two Traditional fields:
Heat:
The energy transferred from one body or system to another as a result of a difference in temperature.
Temperature:
The property of a body or region of space that determines whether or not there will be a net flow of heat into it or out of it from a neighboring body or region and in which direction (if any) the heat will flow.
If there is no heat flow the bodies or regions are said to be in thermal equilibrium and at the same temperature. If there is a flow of heat, the direction of the flow is from the body or region of higher temperature.
Energy:The capacity of a physical system to do work.SI unit for energy is the joule (J) or watt-sec.
A system can have energy in a variety of forms
- Kinetic Energy due to its motion
- Potential Energy due to the positions
- Chemical Energy stored in chemicals
Thermodynamics: Concerned with the nature of heat , its measure and conversion to mechanical, electric, and chemical energy, laws governing the Heat Energy.
SUMMARY:
- Importance and application of thermal analysis for design If there is no heat flow the bodies or regions are said to be in thermal equilibrium and at the same temperature.
- If there is a flow of heat, the direction of the flow is from the body or region of higher temperature.
- Thermodynamics: Concerned with the nature of heat,its measure and conversion to mechanical, electric,and chemical energy, laws governing these.
-























0 Comments